India–EU “Mother of All Trade Deals”: Boon or Bane for the Oil & Gas Sector?
New Delhi and Brussels have concluded a comprehensive pact that sharply cuts tariffs and expands market access across most goods and sectors. While attention is on manufacturing and services, the oil and gas industry will also see meaningful impacts, as tariff reductions extend to energy-related products, petrochemicals, and equipment used in exploration, refining, and transport.
- Greater Market Access and Tariff Reductions: For the oil and gas sector, which relies heavily on imported technology, advanced materials and spare parts, these changes could incrementally reduce operating expenses and improve competitiveness.
- Investment and Technology Flows: A cornerstone of the new trade pact is enhanced investment protection and facilitation, alongside accelerated regulatory cooperation.European firms are global leaders in refining technology, LNG infrastructure, floating storage units, turbine manufacturing and carbon capture systems. Improved investment protections could encourage EU firms to invest in or partner with Indian oil & gas companies, particularly in refining, petrochemicals and downstream processing.
- New generation energy technology: India’s strategic energy transition goals including lower carbon fuels, hydrogen value chains and clean energy infrastructure align with Europe’s technological strengths. Easier capital flows under the FTA could help accelerate adoption of next-generation energy technology.
- Competitive Dynamics in Refining and Petrochemicals: India is a major global refining hub but still depends on imported equipment and catalysts, largely from Europe. Lower import duties could accelerate refinery upgrades and improve global competitiveness. At the same time, cheaper European petrochemical imports may intensify competition in India and the EU, pushing Indian refiners to focus on scale, efficiency, and niche, high-value products.
- Strategic Energy Cooperation Beyond Goods: Though the agreement is primarily trade focused, its broader economic cooperation provisions including regulatory harmonisation and services liberalisation could have secondary impacts on the energy sector:
- LNG trade and shipping services: EU maritime and logistics firms may find expanded opportunities in India’s liquefied natural gas (LNG) import and coastal shipping sectors.
- Professional services and project management: With services market access liberalised, EU engineering, construction and project consultancy firms could participate more directly in India’s midstream and downstream infrastructure build-out.
- Geopolitical Significance and Supply Chain Security: The India-EU deal comes at a time of global trade tensions and shifting energy geopolitics including increased tariffs from the U.S. on Indian imports as part of broader geopolitical friction.
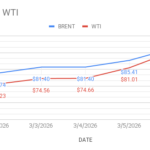
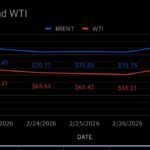
- Boost to LNG : Diversification of partners reduces reliance on single markets, strengthening resilience. Stronger Indo-European trade ties may encourage long-term LNG supply agreements and collaboration on energy transition technologies such as hydrogen, carbon capture, and deep decarbonisation efforts.